Sensors are increasingly being used in a growing number of everyday applications to collect data, for analysis and process improvements. This is particularly true in industrial automation, access control, security systems and healthcare, among many others.
Gathering data from different sensors and then combining it to generate an accurate representation of a setup or a network of systems is called “sensor fusion”. To increase its intelligence and reliability, deep learning algorithms are increasingly applied, to more accurately predict abnormal behaviour in industrial machinery, tools and processes and thus anticipate and prevent failures and damage, which saves time and costs and improves safety.
At the heart of sensor fusion networks (Figure 1) are smart sensors, and they can fit into one or more category:
- Redundant sensors: All sensors give the same information to the world.
- Complementary sensors: The sensors provide separate information about the world.
- Coordinated sensors: The sensors collect information about the world sequentially.

Figure 1: An example of a sensor fusion network setup
All these sensors are linked via a communications backbone, which could be connected in any one of the following schemes:
- Decentralised: No communication exists between sensor nodes.
- Centralised: All sensors provide measurements to a central node.
- Distributed: The nodes interchange information at a given communication rate (e.g., every five scans, or one-fifth communication rate).
The centralised scheme can be regarded as a special case of the distributed scheme, where sensors communicate every so often with one another; see Figure 2.
For the sensor fusion network to be effective, precisely calibrated and synchronised sensors are crucial.

Figure 2: From Industry 4.0 perspective, feedback from one sensor is typically not enough, particularly for the implementation of control algorithms
Deep learning
Performing late fusion allows for interoperable solutions, whereas early fusion gives AI-rich data for predictions.
Latest techniques involve time and space synchronisation of all onboard sensors before feeding synchronised data to a neural network for predictions. This data is then used for AI training or Software-In-the-Loop (SIL) testing of real-time algorithms that receive just a limited piece of information.
Deep learning aims to simply express complicated data. It relies on neural networks to enable computational platforms such as Renesas RA MCU and RZ MPU to train and execute tasks. The neural networks consist of many processing layers, arranged to learn data representations with varying levels of abstraction from sensor fusion. The more layers in the deep neural network, the better the training of the network, and the more accurate the learned representations become.
Multi-stream approaches are successful in neural-network-based multi-modal data fusion. This way, neural networks can be trained and used on MCU-based endpoint applications, helping simplify setups and reducing costs, which in turn will accelerate their adoption in industrial applications.
When combined with AI modelling tools, the Renesas RA MCU platform and its Flexible SW Package help build a multi neural network layer structure.
Renesas offerings
The flexible Renesas Advanced (RA) microcontrollers are 32-bit and highly suitable for smart sensor networks. Renesas also offers a reference design for a versatile Artificial Internet of Things (AIoT) sensor board solution. It targets applications in industrial predictive maintenance, smart home/IoT appliances with gesture recognition, wearables (activity tracking), and innovative HMIs like the FingerSense solution. Renesas provides the complete range of devices, including an IoT-specified RA microcontroller, an array of sensors (air quality, light, temperature, humidity, etc.), a 6-axis inertial measurement unit and cellular or Bluetooth communication support.

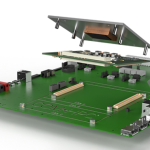
Figure 3: Example of an IIoT-enabled platform by Renesas
For example, the Renesas intelligent condition-monitoring box (Figure 3) is designed for machines condition monitoring based on fusing data from vibration, sound, temperature and magnetic field sensors. Additional sensor modalities for monitoring acceleration, rotational speeds and shock and vibration can also be included.
The system implements sensor fusion through AI algorithms to classify abnormal operating conditions with better granularity, for better decision making. This edge AI architecture can simplify the handling of big data provided by sensors, ensuring that only the most relevant data is sent to the edge AI processor or the cloud for further analysis and the training of ML algorithms.
In summary, implementing AI-based deep learning in industrial applications offers several benefits:
- The AI algorithm can employ sensor fusion to use data from one sensor to compensate for weaknesses in data from another sensor.
- The AI algorithm can classify the relevance of each sensor to specific tasks, and minimise or ignore data from sensors classified as less important.
- Through continuous training at the edge or in the cloud, AI/ML algorithms can learn to identify changes in system behaviour that were previously unrecognised.
- The AI algorithm can predict possible sources of failures, enabling preventative maintenance and improving overall productivity.
Sensor fusion combined with AI deep learning presents a powerful tool to maximise the benefits when using a variety of sensor modalities. AI/ML-based enhanced sensor fusion can be employed at several levels in a system, including at the data, fusion or decision levels. Basic functions in sensor fusion implementations include smoothing and filtering sensor data and predicting sensor and system states.
By Suad Jusuf, Senior Manager, Renesas